Blog
-
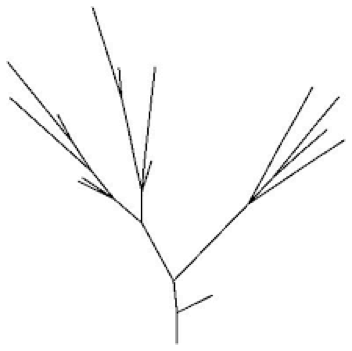
Phase transition, scaling of moments, and order-parameter distributions in Brownian particles and branching processes with finite-size effects
Posted on
by
Random walks provide precise mathematical models for diffusion processes, while rooted trees offer a geometric representation of branching processes. Both are of broad importance in probability theory and statistical physics, and some important mathematical results establish links between the two.
-
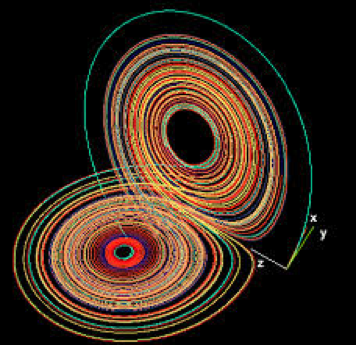
Predicting chaos with an optimal combination of data and prior knowledge
Posted on
by
Early in the 20th century, experts tried to forecast the weather by noting current conditions, patterns of winds, temperatures and air pressures, and looking into historical records to find previous moments when similar conditions prevailed. Looking a few days forward in the
-
Synchronisation and Extreme Value Theory for Coupled Map Lattices
Posted on
by
Coupled Map Lattices (CML) are discrete time and space dynamical systems often used as simplified models for the study of spatially-extended non-linear systems.
-
Weak Galilean invariance as a selection principle for coarse-grained diffusive models
Posted on
by
Galileo Galilei famously stated the principle of Galilean invariance, which links the equations of motion of closed systems as viewed in distinct inertial frames translating relative to one another at a constant velocity.
-
Universal behavior of the full particle statistics of one-dimensional Coulomb gases with an arbitrary external potential
Posted on
by
Random matrix theory is central to the study of the properties of strongly correlated systems in condensed matter physics and related fields, where important physical quantities are surprisingly well reflected by the joint probability density of the eigenvalues of random matrices.
-
Intermittent dynamics in complex systems driven to depletion
Posted on
by
From earthquakes driven by continental drift to businesses altering their strategies in response to customers’ behaviour, many complex systems exhibit highly unpredictable dynamics, fluctuating episodically between periods of relative quiescence and bursts of activity.
-
Heteroclinic networks – probing the hidden influence of unstable fixed points
Posted on
by
The stable fixed points of a dynamical system attract obvious interest as potential resting points, or final states. Without continued forcing, for example, a physical pendulum will ultimately end up hanging motionless in the downward position.
-
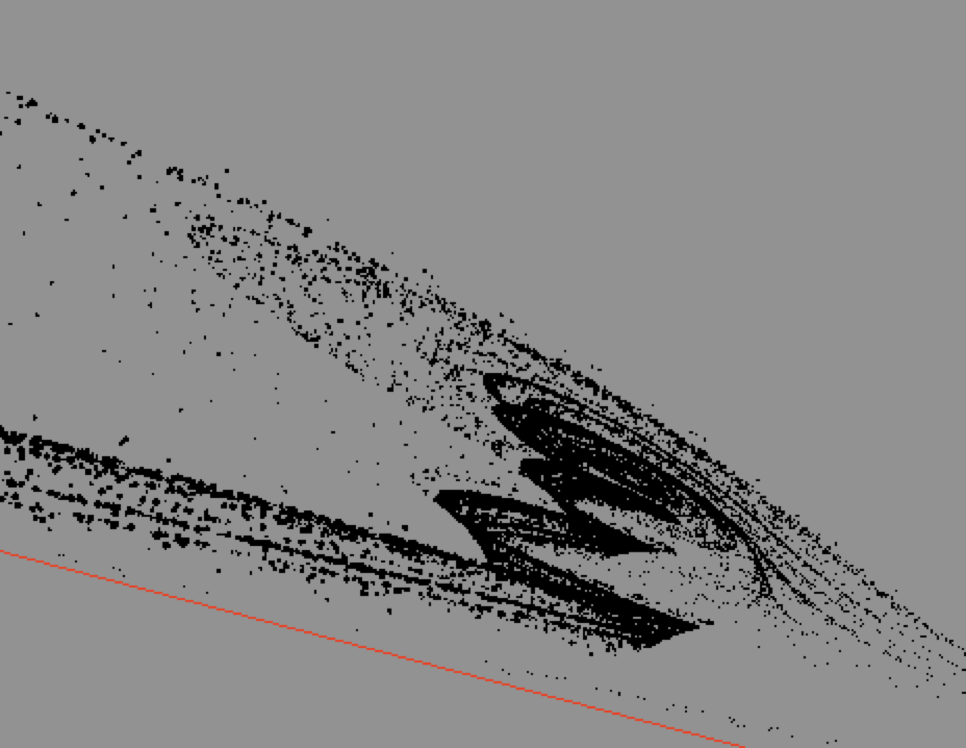
Using Extreme Value Theory to Characterize Chaotic Dynamics
Posted on
by
In the analysis of dynamical systems, the correlation dimension is a useful indicator describing the fractal structure of invariant sets. Other measures, such as the Lyapunov exponents and the entropy, provide complementary information on the time scale of predictability of the system.
-
Characterizing local energy transfers in atmospheric flows
Posted on
by
Computational models employed for simulations of weather and climate have limited spatial resolution, currently around 2 km for regional weather models and 100 km for global climate models.
-
LML External Fellow Davide Faranda has received the 2018 Outstanding Early Career Scientists Award of the European Geosciences Union
Posted on
by
Davide was given the award for “his exceptional contributions to developing the theory of extreme values for dynamical systems and its use for analysing the underlying properties of the dynamics of the atmosphere and the climate system.”