Blog
-
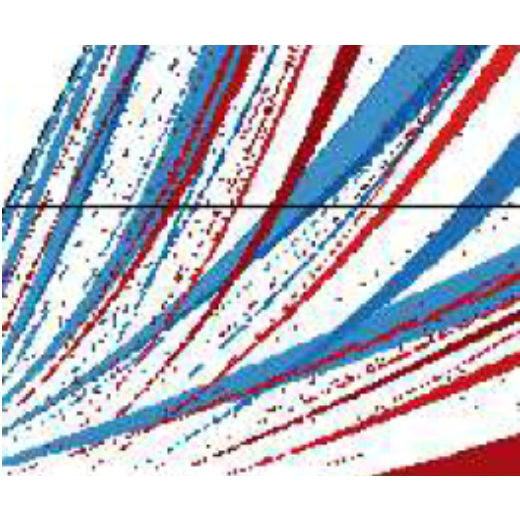
Normal and Anomalous Diffusion in Soft Lorentz Gases
Posted on
by
Engineered nanoscale structures known as artificial graphene exhibit the properties of real graphene but in a setup where it is easy to tune features such as the electronic density, lattice constant, geometry or coupling with the environment.
-
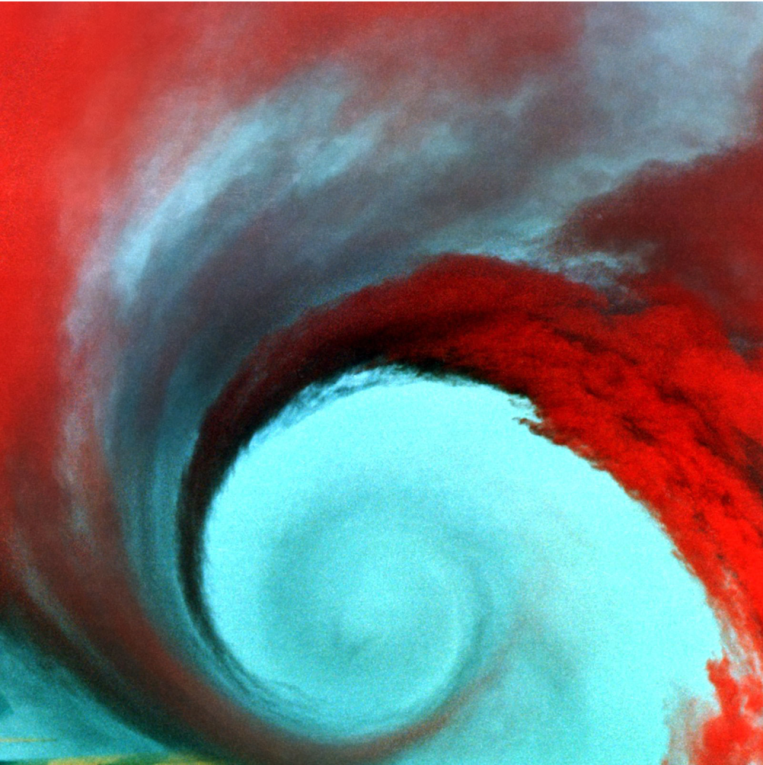
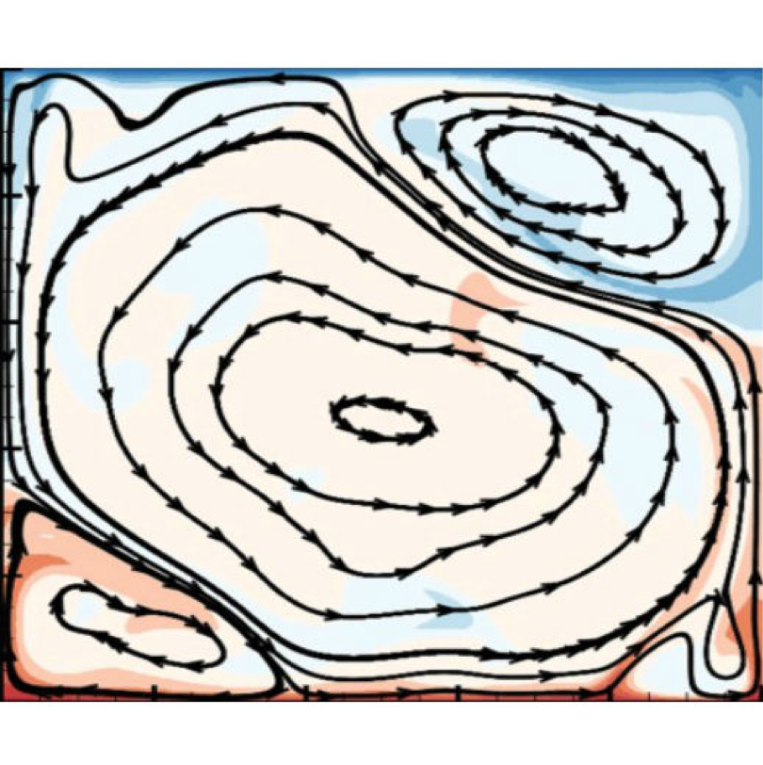
On reversals in 2D turbulent Rayleigh-Bénard convection: Insights from embedding theory and comparison with proper orthogonal decomposition analysis
Posted on
by
In the 1980s, most researchers approached empirical analysis of low-dimensional dynamical systems through the famous Takens embedding theorem, which guarantees that the attractor of any dynamical system can be reconstructed from samples of the values of key variables.
-
The LML has hired External Fellow Erica Thompson as Principal Investigator of Inference from Models
Posted on
by
Erica’s research focusses on subtle issues affecting the use of mathematical models and simulations in aid of real-world decision making. In her own words,
-
The hammam effect or how a warm ocean enhances large scale atmospheric predictability
Posted on
by
Will climate change make weather forecasting harder than it currently is? Or, could a warmer planet make prediction easier? The answer isn’t obvious. Because atmospheric dynamics are chaotic, there are practical limits to predictability, regardless of data precision and available computing power.
-
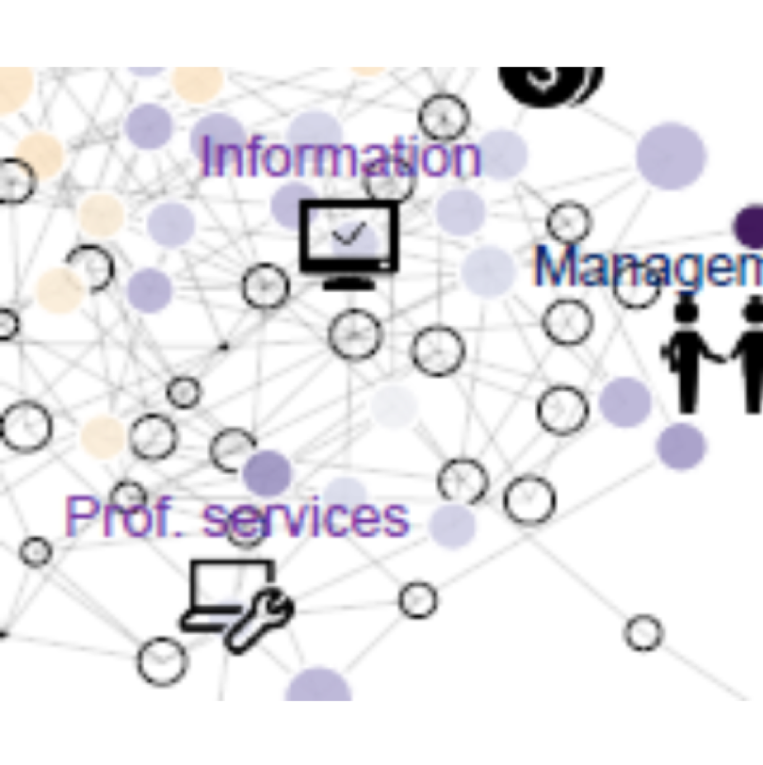
Common Trajectories for Urban Economies
Posted on
by
Large cities play a disproportionate role in global economic productivity and innovation. Their productivity advantage rests on specialization and the concentration of many diverse skills and capabilities in one place, multiplying economic opportunities and efficiencies. Even so, cities do not appear to
-
LML Fellow Rainer Klages has been awarded a Mercator Fellowship to support an 8-month guest professorship at the Technical University of Berlin
Posted on
by
Rainer was recently nominated for the Fellowship by the Institute of Theoretical Physics at the Technical University of Berlin. The Fellowship will support a guest professorship, enabling him to work with scientists of the German Collaborative Research Centre ‘Control of self-organising nonlinear
-
Conditioned Lyapunov exponents for random dynamical systems
Posted on
by
Lyapunov exponents play a central role in dynamical systems theory, and offer a measure of the local instability that lies behind deterministic chaos and the sensitive dependence of trajectories on initial conditions.
-
Agreement between LML and the National Autonomous University of Mexico to fund a postdoctoral research assistant.
Posted on
by
The London Mathematical Laboratory has signed a new research agreement with the Institute of Physics at the National Autonomous University of Mexico (UNAM) in Mexico City.
-
A test on methods for complete magnitude estimation based on earthquake catalogues
Posted on
by
Earthquake statistics follow an approximate scaling law – the famous Gutenberg-Richter law – which states that the number of earthquakes having magnitude m larger than some value M falls off as a power law with an exponent b. The value of b
-
Spectra of Sparse Non-Hermitian Random Matrices
Posted on
by
Random matrix theory starts from the assumption that the large-scale behaviour of a complex system should be governed by its symmetries and the statistical properties of its parameters, and be relatively insensitive to the precise details of each interacting element.