Author: LML administrator
-
Big jump principle for heavy-tailed random walks with correlated increments
Posted on
by
Since its first formulation in 1964, the so-called “big jump principle” (BJP) of extreme value statistics has played an important role in fields such as large deviation theory and financial mathematics. For heavy-tailed distributions, the principle considers N independent and identically distributed
-
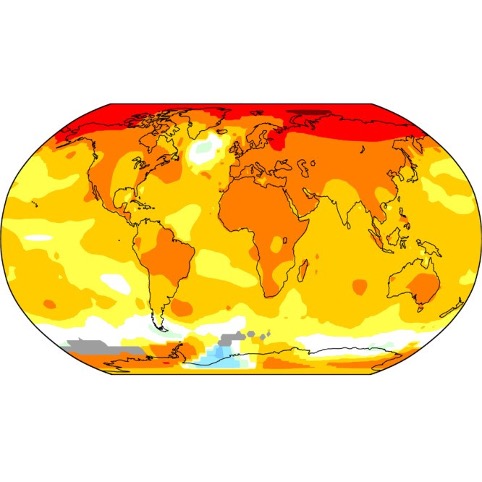
On Generalized Langevin Dynamics and the Modelling of Global Mean Temperature
Posted on
by
For more than half a century, researchers have employed mathematical models to better understand the response of the Earth’s climate to internal fluctuations as well as external perturbations, whether anthropogenic or solar. These models range from highly complex and multi-dimensional general circulation
-
Analytic approach for the number statistics of non-Hermitian random matrices
Posted on
by
The study of random matrices finds many important applications in physics, mathematics, biology, statistics and finance, as random matrix ensembles offer simple but nontrivial models of strongly correlated systems.
-
Decision-making with distorted memory: Escaping the trap of past experience
Posted on
by
Humans make decisions in part by drawing on their previous related experiences. But human memory isn’t exhaustive and complete.
-
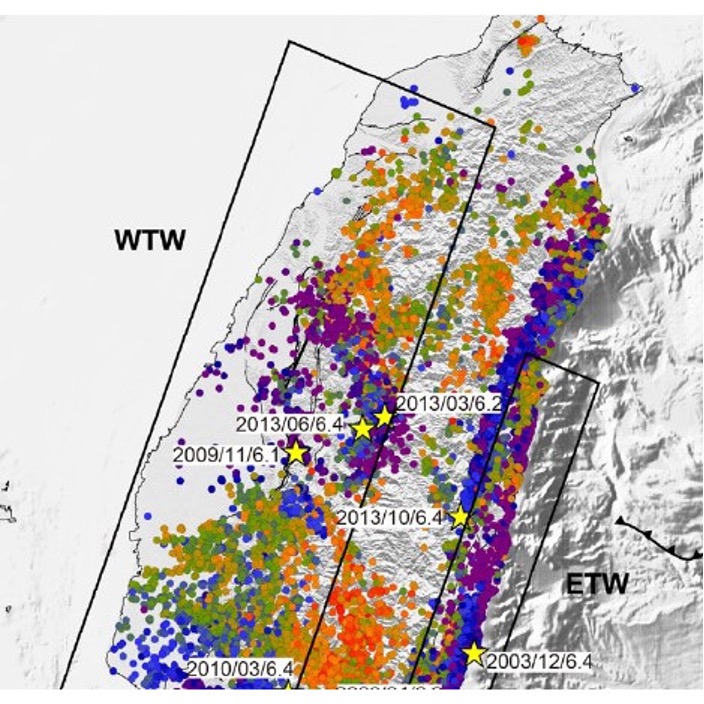
Synchronized and asynchronous modulation of seismicity by hydrological loading: A case study in Taiwan
Posted on
by
Many distinct physical factors help trigger earthquakes, among them the loading of the earth’s crust by water. Many studies have demonstrated a seasonal modulation of seismicity linked to water forcing in volcanic areas, plate boundary zones and other regions.
-
Urban Science: Integrated Theory from the First Cities to Sustainable Metropolises
Posted on
by
The emergence of cities is a relatively recent phenomenon in human history. Their appearance in the archaeological record coincides with the advent of increasingly sedentary, agricultural, bureaucratic, and politically asymmetrical societies.
-
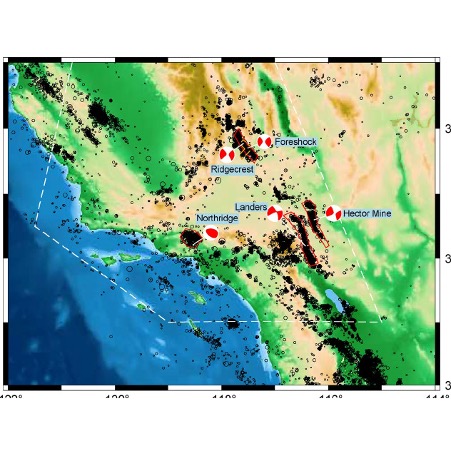
Ranking earthquake forecasts using proper scoring rules: binary events in a low probability environment
Posted on
by
Probabilistic earthquake forecasts estimate the spatial and/or temporal evolution of seismicity and offer practical guidance to authorities during earthquake sequences, especially following notable earthquakes.
-
Root and community inference on latent network growth processes using noisy attachment models
Posted on
by
Complex networks can be analysed using a variety of statistical models including classic Erdös–Rényi random graphs, latent space models, configuration graphs and others. These models generally specify some structure – arising from the existence of communities, for example – but the order
-
Detecting intense hurricanes from low resolution datasets via dynamical indicators
Posted on
by
Tropical cyclones are among the most extreme and costly weather events. In the United States, hurricane Katrina in 2005 alone caused damage equal to roughly 1% of the country’s gross domestic product.
-
Heterogeneity of Aftershock Productivity Along the Mainshock Ruptures and Its Advantage in Improving Short-Term Aftershock Forecast
Posted on
by
Large earthquakes generate aftershocks, the spatiotemporal patterns of which reveal details of how the strain energy in the Earth’s crust relaxes following a main rupture. Prior research has established that aftershocks correlate with regions of low co-seismic slip – slip which occurs