Blog
-
Urban Science: Integrated Theory from the First Cities to Sustainable Metropolises
Posted on
by
The emergence of cities is a relatively recent phenomenon in human history. Their appearance in the archaeological record coincides with the advent of increasingly sedentary, agricultural, bureaucratic, and politically asymmetrical societies.
-
Ranking earthquake forecasts using proper scoring rules: binary events in a low probability environment
Posted on
by
Probabilistic earthquake forecasts estimate the spatial and/or temporal evolution of seismicity and offer practical guidance to authorities during earthquake sequences, especially following notable earthquakes.
-
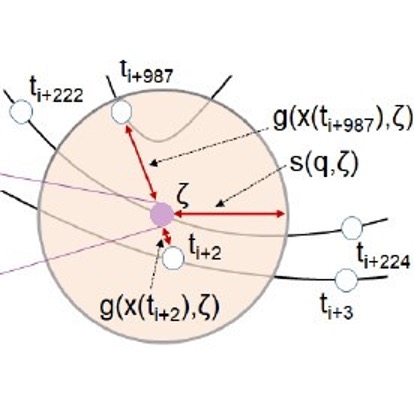
Root and community inference on latent network growth processes using noisy attachment models
Posted on
by
Complex networks can be analysed using a variety of statistical models including classic Erdös–Rényi random graphs, latent space models, configuration graphs and others. These models generally specify some structure – arising from the existence of communities, for example – but the order
-
Detecting intense hurricanes from low resolution datasets via dynamical indicators
Posted on
by
Tropical cyclones are among the most extreme and costly weather events. In the United States, hurricane Katrina in 2005 alone caused damage equal to roughly 1% of the country’s gross domestic product.
-
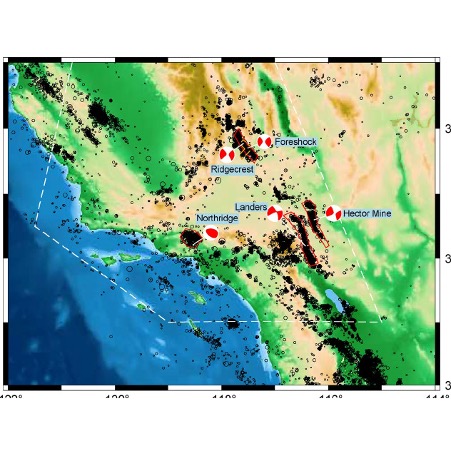
Heterogeneity of Aftershock Productivity Along the Mainshock Ruptures and Its Advantage in Improving Short-Term Aftershock Forecast
Posted on
by
Large earthquakes generate aftershocks, the spatiotemporal patterns of which reveal details of how the strain energy in the Earth’s crust relaxes following a main rupture. Prior research has established that aftershocks correlate with regions of low co-seismic slip – slip which occurs
-
Magnetic reconnection, the existential risks of searching for alien civilizations and carbon emissions in Africa
Posted on
by
Here are links to a few recent articles by LML External Fellow Mark Buchanan.
-
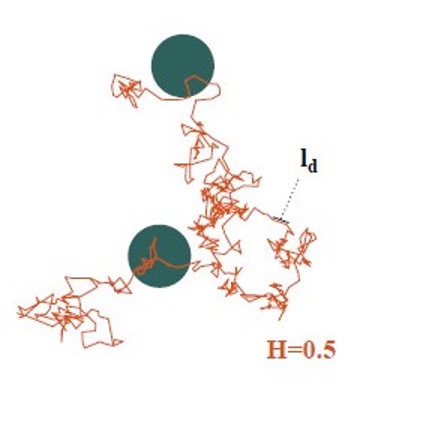
Search efficiency of discrete fractional Brownian motion in a random distribution of targets
Posted on
by
In foraging for food, biological organisms explore terrain in search of irregularly dispersed sources. Mathematically, such foraging processes can be modelled using stochastic processes, and in the simplest paradigm – Gaussian spreading generated by random walks or Brownian motion – the mean
-
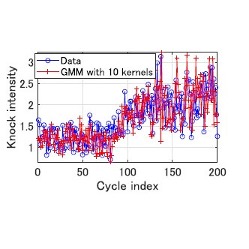
Statistical simulator for the engine knock
Posted on
by
Although the automotive industry is rapidly shifting to electric cars, Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs) – with both an electric motor and an internal combustion engine – will still dominate for the next half century.
-
Anomaly detection and classification in traffic flow data from fluctuations in the flow–density relationship
Posted on
by
An important goal in highway traffic management is event detection – finding ways to use real-time data to alert authorities to potential problems as they begin to emerge.
-
Uncertainty relation between detection probability and energy fluctuations
Posted on
by
A particle following a classical random walk on a finite graph will explore the system completely, in time visiting every site repeatedly. The process is ergodic.