Blog
-
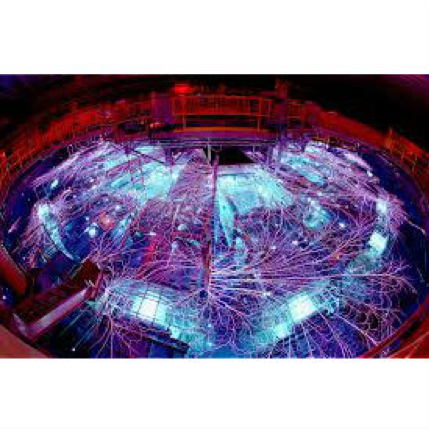
The aromatic universe, new hope for public transport, and why we’re still years away from practical fusion energy
Posted on
by
Here are links to a few recent articles by LML External Fellow Mark Buchanan.
-
Seismological investigations of induced earthquakes near the Hutubi underground gas storage facility
Posted on
by
Earth scientists have long known that fluid injected into the Earth’s crust can induce earthquakes. In principle, seismic activity may also be triggered through gas extraction through the mechanism of poroelastic stress perturbation, although such events have been observed less frequently.
-
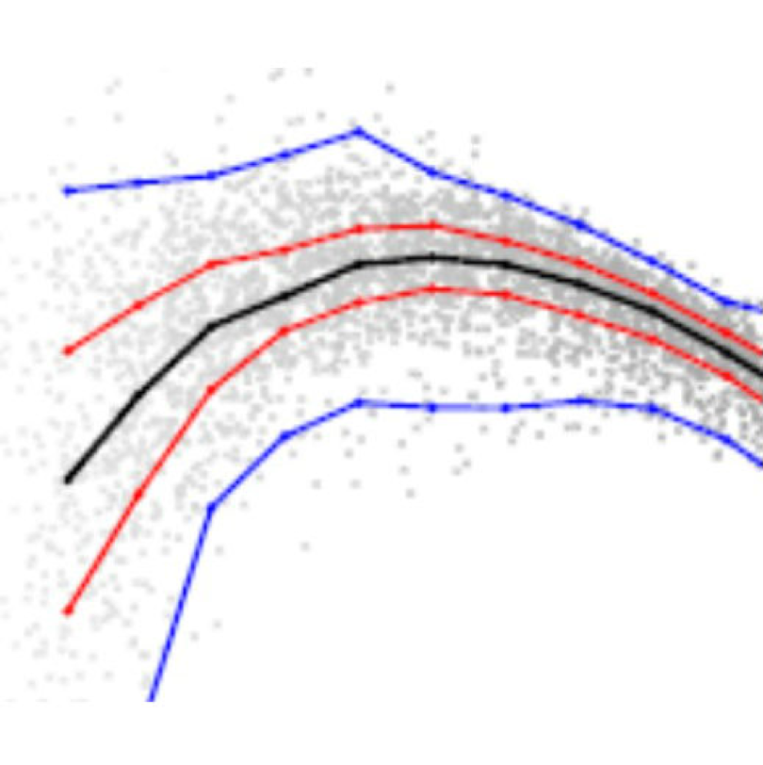
Minimal dynamical systems model of the Northern Hemisphere jet stream via embedding of climate data
Posted on
by
Jet streams are narrow, fast-flowing westerly air currents located near the tropopause, the tropospheric boundary with the higher stratosphere. These jets play a major role in driving the large-scale atmospheric circulation and modulate the frequency, severity and persistence of weather events at
-
Spectral theory for the stability of dynamical systems on large oriented locally tree-like graphs
Posted on
by
The linear stability of large complex systems around their stationary points can be studied with random matrix theory. In one common model, the i.i.d. random matrix model, one assumes a simple statistical form for the interactions between distinct elements of a network.
-
New experiments back Ergodicity Economics over Expected Utility Theory in modeling human decision making
Posted on
by
Economists thinking about anything from housing policy to climate change need to model how people make decisions, especially when facing uncertainty and risk.
-
Interview with Marc Elsberg, author of the new German language novel Gier.
Posted on
by
Economics had its critics even before the financial crisis of a decade ago. Since then doubt has grown over how much economists really know. Much of economics rests on analyses of how individuals – as consumers, or in managing a business, for
-
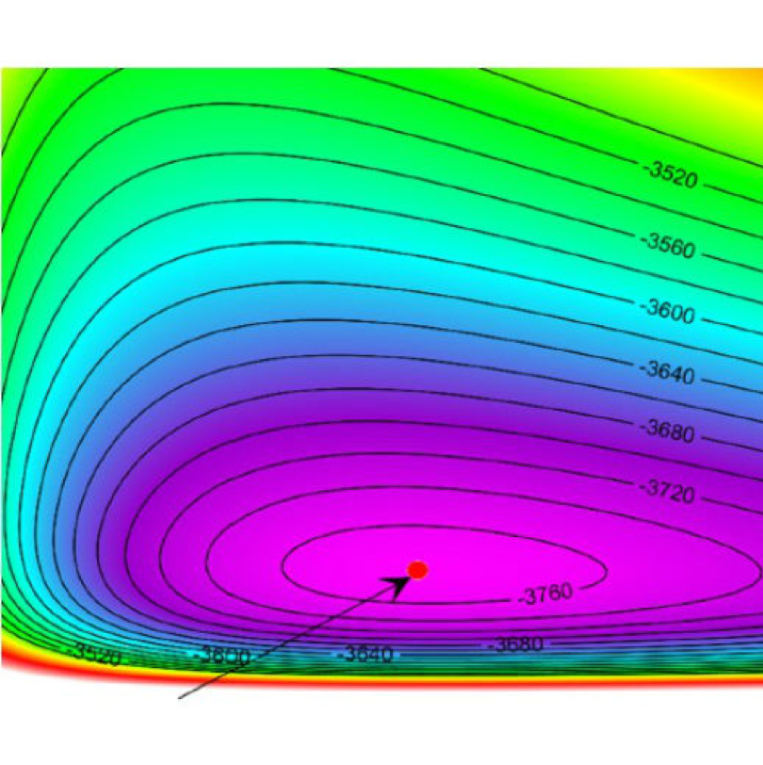
Bayesian approach for network adjustment for gravity survey campaign: methodology and model test
Posted on
by
Variations in the strength of gravity over the Earth’s surface reflect underlying geophysical changes such as groundwater change, surface vertical deformation, tectonic events, earthquakes and other processes. To study such processes, so-called gravity survey campaigns collect observations made repeatedly at fixed stations.
-
Data Science for Social Good (DSSG) Summer Fellowship programme
Posted on
by
High-profile data horror stories are becoming increasingly common, from Facebook’s relationship with Cambridge Analytica to the leak of UK diplomatic cables and massive security breaches at some of the world’s biggest companies.
-
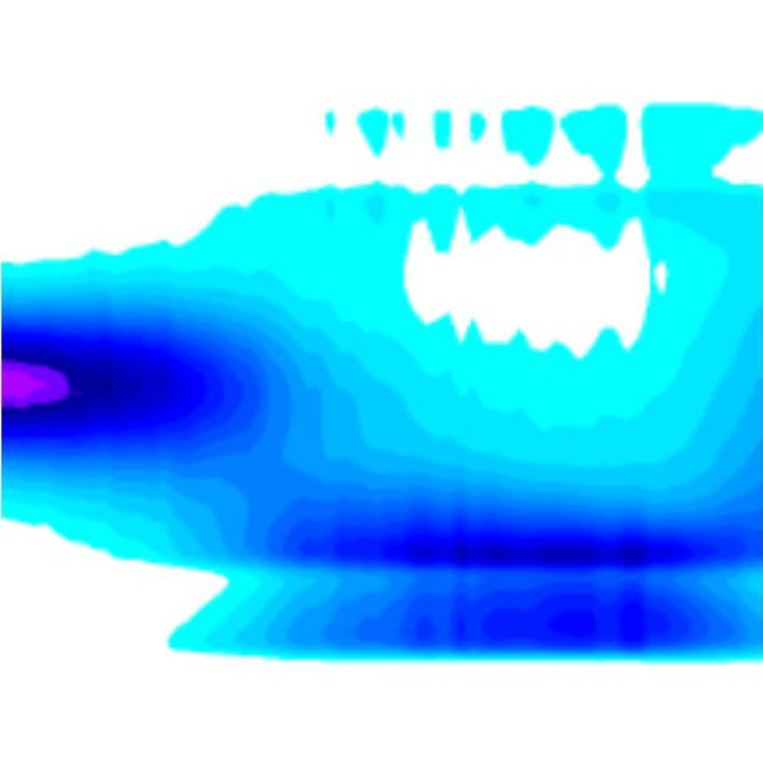
Scale interactions and anisotropy in stable boundary layers
Posted on
by
Some of the strongest challenges for numerical weather prediction come from the unsteady nature of certain flows, in particular nocturnal and stable boundary layers.
-
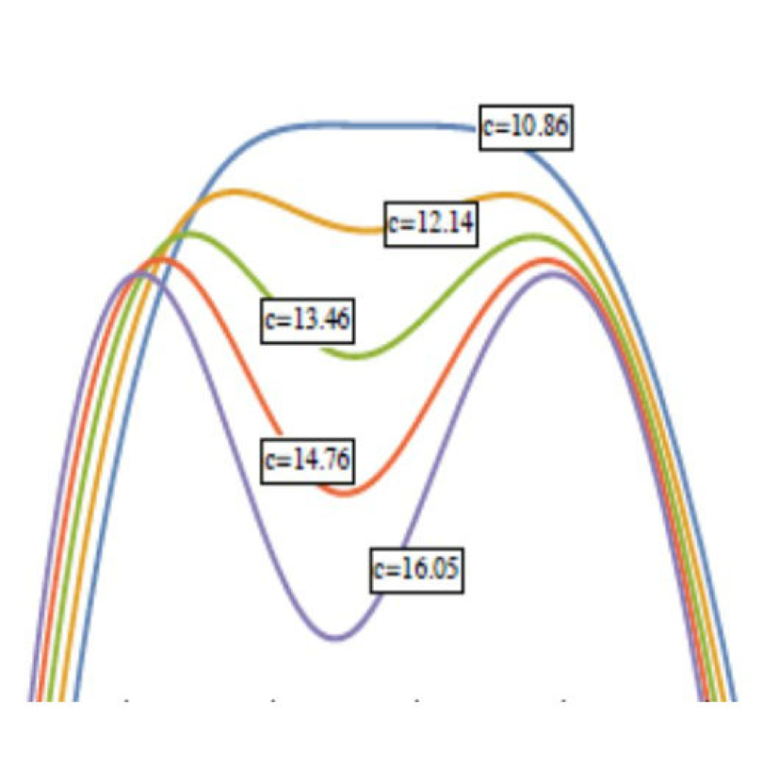
Condensation of degrees emerging through a first-order phase transition in classical random graphs
Posted on
by
When steam condenses from vapour into liquid, the water molecules move closely together and the system, from a mathematical point of view, comes to reside in an extremely small portion of the conceptually available phase space.