Author: LML administrator
-
Machines learn from biology, the speed of coronavirus and how to build an ethical self-driving ca
Posted on
by
Here are links to a few recent articles by LML External Fellow Mark Buchanan.
-
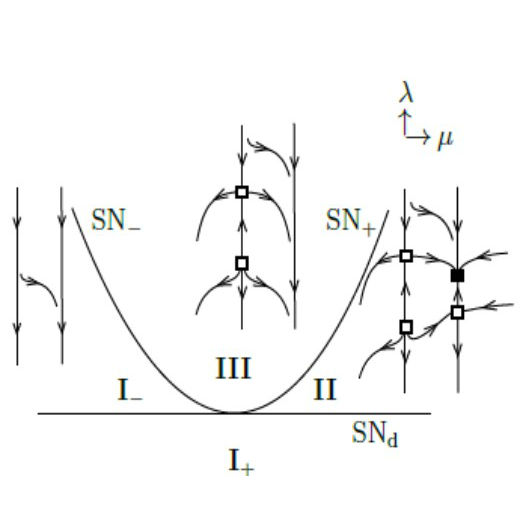
Bifurcations on Fully Inhomogeneous Networks
Posted on
by
One of the most powerful methods of bifurcation theory is centre manifold reduction, in which a judicious coordinate change greatly simplifies the analysis of dynamical systems in the vicinity of a bifurcation point.
-
Superextreme Waves Generation in the Linear Regime
Posted on
by
So-called extreme or rogue waves are large amplitude waves which appear unpredictably in optical and acoustic systems, in plasmas, as well as in quantum physics and in hydrodynamics.
-
Should We Be Afraid of Artificial Intelligence?
Posted on
by
Economists worry about the impact that artificial intelligence (AI) technology could have as it begins to displace human employees, especially those in entry-level jobs such as data entry, customer service or retail.
-
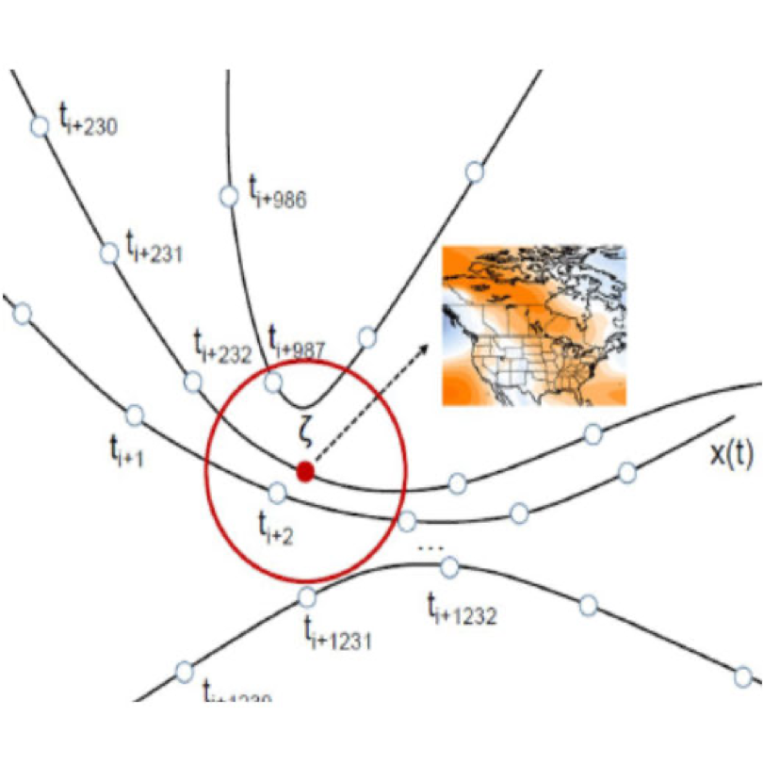
Diagnosing concurrent drivers of weather extremes: application to warm and cold days in North America
Posted on
by
Extreme weather events emerge out of the interaction of many physical processes, and understanding how is a key challenge in atmospheric science.
-
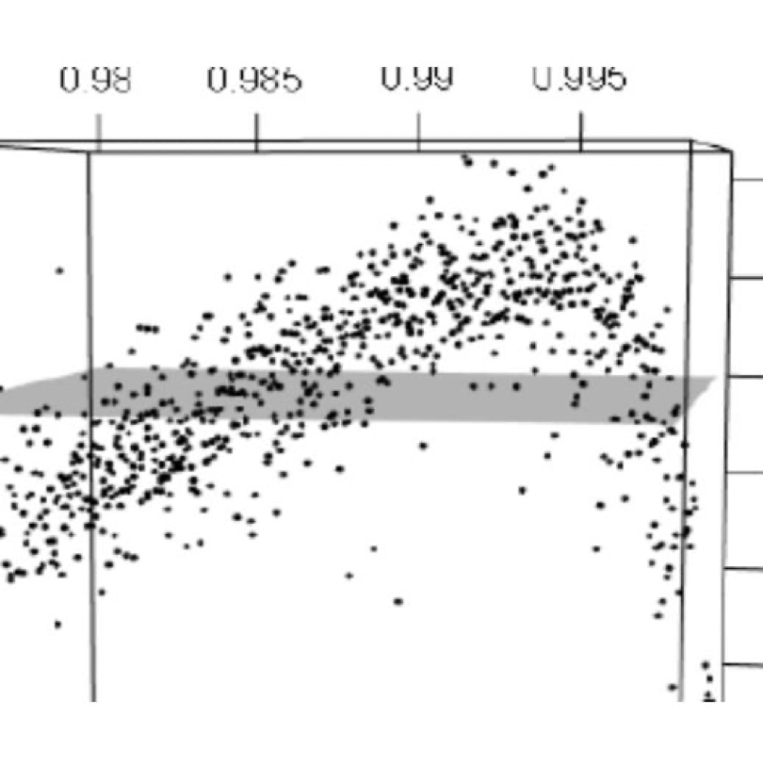
Sampling hyperspheres via extreme value theory: implications for measuring attractor dimensions
Posted on
by
Advancing computational power has encouraged the analysis of large, high-dimensional data sets with machine learning and data mining techniques, as well as the use of algorithms to compute dynamical indicators such as Lyapunov exponents or generalized dimensions.
-
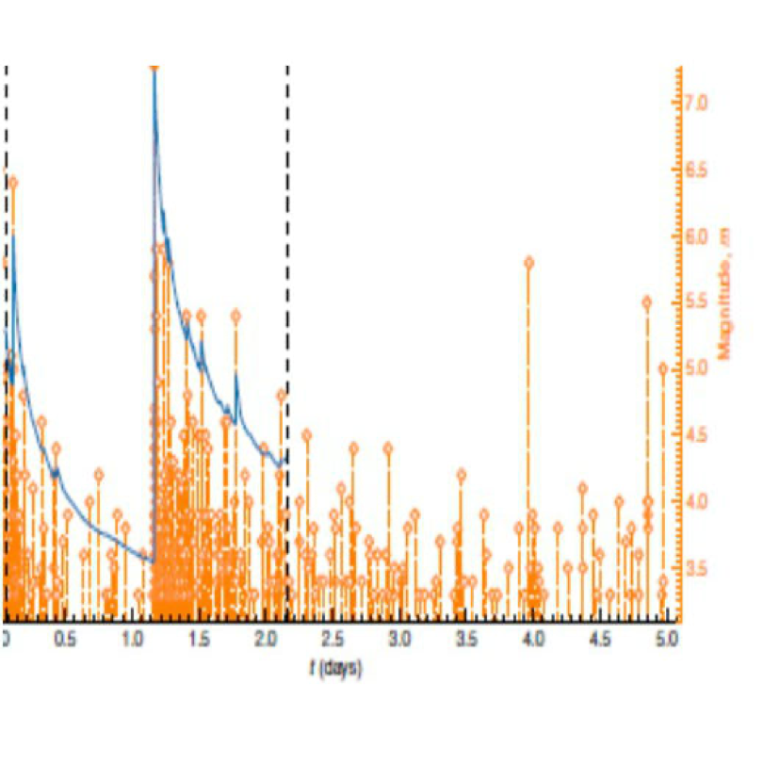
Forecasting the magnitude of the largest expected earthquake
Posted on
by
Geophysicists still lack a comprehensive understanding of the mechanisms and stochastic dynamics behind the earthquake generation process, and so also lack an ability to make reliable predictions of the likelihood of extreme events.
-
Epidemic spreading with awareness and different timescales in multiplex networks
Posted on
by
Efforts to control epidemics rely on mathematical and computational models of how infectious agents spread. Such models help to find ways to deter transmission – through vaccination and quarantine, for example, or information campaigns to alter human behaviour.
-
Age representation of Lévy walks: partial density waves, relaxation and first passage time statistics
Posted on
by
Mathematical models of Lévy Walks have found many recent applications to physical and biological systems, and such applications have generally approached Lévy Walks from the traditional perspective of discrete models for random walks.
-
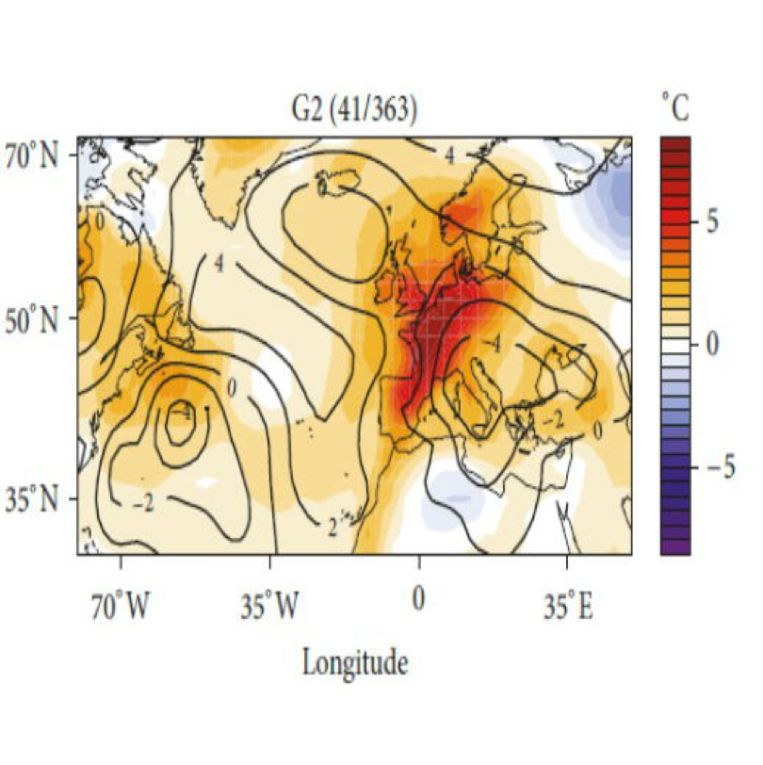
Atmospheric Dynamics Leading to West European Summer Hot Temperatures Since 1851
Posted on
by
In Western Europe, several recent summers have been exceptionally warm, especially the summers of 2003 and 2015. Based on observations over the past century, meteorologists have come to see such major heat events as typically stemming from anticyclonic atmospheric circulation and a